A Deep Dive into Generative AI Engine Optimization for Local Businesses: Actionable Strategies for AI-Driven Visibility
I. Introduction: Navigating the New Search Frontier
The Evolution of Search: From Traditional SEO to Generative [AI] Engine Optimization (GEO)
The digital landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the rapid advancements in Artificial Intelligence. Traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO), which has historically focused on keyword matching and backlink profiles to improve rankings on search engine results pages (SERPs), is now evolving. Generative [AI] Engine Optimization (GEO) is emerging as the new paradigm, aligning content with the needs of sophisticated AI-powered search engines. These include platforms like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), also known as AI Overviews, as well as conversational AI interfaces like ChatGPT and Bing Chat.
This fundamental shift means that search engines are no longer merely indexing web pages to provide lists of links. Instead, they are actively generating comprehensive, contextual answers directly in response to user queries. The primary objective in this new environment is for a business’s content to become the authoritative source that AI systems cite, summarize, or directly present in their generated responses. This represents a significant departure from the traditional goal of simply ranking high on a list of search results.
The digital landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the rapid advancements in Artificial Intelligence. Traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO), which has historically focused on keyword matching and backlink profiles to improve rankings on search engine results pages (SERPs), is now evolving. Generative [AI] Engine Optimization (GEO) is emerging as the new paradigm, aligning content with the needs of sophisticated AI-powered search engines. These include platforms like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), also known as AI Overviews, as well as conversational AI interfaces like ChatGPT and Bing Chat.
This fundamental shift means that search engines are no longer merely indexing web pages to provide lists of links. Instead, they are actively generating comprehensive, contextual answers directly in response to user queries. The primary objective in this new environment is for a business’s content to become the authoritative source that AI systems cite, summarize, or directly present in their generated responses. This represents a significant departure from the traditional goal of simply ranking high on a list of search results.
Why GEO is Critical for Local Businesses in the AI Era
Local businesses, in particular, face a critical need to adapt to this evolving search landscape. AI-driven results (often referred to as Generative AI Results or GAIRs) provide concise answers and summaries sourced from across the web, which can significantly alter the traditional click-through model. This means that users may obtain the information they need directly from the AI overview without ever needing to click through to an individual business’s website. This phenomenon can lead to decreased website traffic, even if a business’s information is accurately cited within the AI summary.
The shift from a “search engine” to an “answer engine” is not a minor update; it represents a fundamental change in how users discover information. For local businesses, where immediate access to information such as operating hours, precise location, and available services is paramount, this “zero-click” behavior is particularly impactful. If a business’s crucial details are not readily available and cited within the AI overview, it risks becoming effectively invisible, regardless of its traditional SEO rankings. This situation creates a heightened sense of urgency for local businesses to prioritize GEO, as their conventional traffic sources are directly threatened.
However, this transformation also presents significant opportunities. Early adoption of GEO practices offers a distinct competitive advantage, enhancing a business’s digital visibility, improving its credibility, and positioning it ahead of competitors in AI-driven search results. By optimizing for AI, local businesses can reach a new segment of users who prefer conversational search and direct answers, potentially outmaneuvering competitors who are slower to adapt. This perspective suggests that GEO is both a necessary defensive strategy to protect existing visibility and an offensive strategy to gain new market share and drive growth. It is about ensuring a brand’s content is accurately interpreted, cited, and presented by AI systems, thereby increasing its overall reach and authority in the evolving digital environment.
II. Understanding Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
What is GEO? Core Concepts and Principles
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a digital marketing strategy specifically designed to enhance the visibility and influence of content within AI-generated responses. It represents a strategic evolution from traditional SEO by moving beyond simple keyword matching. Instead, GEO focuses on deeply understanding user intent and the contextual relevance of content. The core principle of GEO involves creating detailed, high-quality information that fits naturally and seamlessly into the comprehensive answers generated by AI-driven search engines. The ultimate goal is to provide users with thorough and accurate answers that precisely match their information needs.
At its foundation, GEO relies heavily on advanced AI and machine learning technologies. These technologies are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data, including complex user queries and their underlying intent, as well as the broader contextual relevance of web content. This analysis enables AI systems to generate highly comprehensive and pertinent responses. Therefore, optimizing for GEO means crafting content that is not only informative but also structured and semantically rich enough for AI systems to easily process, interpret, and integrate into their generated outputs.
Key Differences: GEO vs. Traditional SEO
While both Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO) share the overarching goal of improving online visibility, their approaches and execution differ significantly. Traditional SEO primarily aims to improve content rankings on standard Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) by optimizing for keywords and backlinks. In contrast, GEO specifically targets AI-driven platforms that generate direct answers to user queries, such as Google’s AI Overviews.
A fundamental distinction lies in the objective: traditional SEO seeks to rank pages, while GEO strives for content to be the direct source that an AI system cites, summarizes, or presents as an answer. This means GEO methods delve much deeper into understanding user intent and behavior, moving beyond the heavy reliance on keyword research and meta tags that characterize traditional SEO.
For local businesses, a particularly crucial difference is GEO’s strong emphasis on geo-targeting. Unlike traditional SEO, which often casts a wider net for global reach, GEO hones in on specific regions and prioritizes local keywords to dominate regional search results. This localized content strategy ensures relevance to specific demographics and often faces less competition in niche local markets, providing a competitive edge.
Furthermore, GEO leverages AI algorithms to generate high-quality content at scale and personalize the user experience, which is a capability not inherent in traditional, manual SEO processes. However, it is important to note that AI-generated content requires careful monitoring to ensure quality and avoid potential SEO risks or generic outputs.
The following table provides a clear comparison of the key distinctions between GEO and traditional SEO:
| Criterion | Traditional SEO | Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) |
| Goal | Improve SERP rankings | Be cited/summarized by AI in direct answers |
| Focus | Keywords, Backlinks, Technical SEO | User Intent, Context, Trust, Semantic Relevance |
| Key Tactics | Manual keyword research, Link building, Meta tags | Structured data, E-E-A-T, Conversational content, Review management |
| Content Approach | Broad reach, Global optimization | Local/Hyperlocal, Comprehensive answers, Human-centered |
| Measurement | Clicks, Impressions, Rankings | AI Citations, Brand Mentions, Conversion quality |
| Competition | High, broad | Niche, often less direct for AI citations |
| Core Technology | Web crawlers, Indexing algorithms | LLMs, RAG, NLP, Knowledge Graphs |
The AI Backbone: How Large Language Models (LLMs), Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Knowledge Graphs Power Generative Search
Generative search experiences are powered by a sophisticated interplay of various AI technologies. Understanding these components is crucial for any local business aiming to optimize its digital presence.
Large Language Models (LLMs): These are advanced AI models trained on immense datasets of text to predict words in sequences, enabling them to generate human-like text, summarize information, translate languages, and classify content. In the context of generative search, LLMs like Google’s Gemini power features such as AI Overviews and AI Mode, transforming standard search results into interactive, AI-generated responses. Similarly, Bing’s Copilot utilizes LLMs to generate summaries from top web search results, providing users with direct answers. These models base their responses on high-signal mentions and properly structured context, considering factors such as user behavior, query context, and geographical location to fine-tune their output.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): RAG is a powerful framework that enhances the capabilities of LLMs by allowing them to fetch real-time information from external data sources. When a user submits a query, the RAG system first searches a designated knowledge base (which can include databases, internal documents, or even the live web) for relevant information. This retrieved context is then added to the original query, creating an “augmented” prompt that the LLM uses to generate its answer. This process significantly improves the accuracy and timeliness of AI-generated content, drastically reducing the likelihood of “hallucinations” (plausible but incorrect answers) and enhancing trust and verifiability by often providing citations. For local businesses, SEO is integral to the success of RAG systems, as content must be optimized for visibility, accessibility, and semantic relevance to ensure effective retrieval by these systems.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is a branch of AI that enables computers to understand, interpret, and interact with human language. In the realm of SEO, NLP techniques are applied to analyze the context, intent, and meaning within user queries and web content, leading to more accurate and relevant search results. NLP plays a pivotal role in enhancing content relevance by matching it precisely with user intent, improving overall user experience, and boosting search rankings by aligning content with how modern algorithms interpret page value. It helps search engines understand semantic connections between words and identify entities such as names, dates, and locations within text. Google specifically uses NLP to determine when generative responses would be most helpful and to extract precise information from webpages for features like AI Overviews and featured snippets.
Knowledge Graphs: The Google Knowledge Graph is a vast database of facts about real-world entities—people, places, organizations, products, and services—that helps Google connect user queries to these entities rather than just matching keywords. It functions as a semantic network, understanding the relationships between different entities. For local businesses, being a verified entity within the Knowledge Graph significantly increases the chances of appearing prominently in various search features, including Knowledge Panels, Image Carousels, Featured Snippets, Voice Search results, and AI summaries. The consistency of online descriptions, the proper use of structured data (Schema.org markup), the presence of Wikidata entries, and consistent information across social media platforms are all crucial sources that shape a business’s entity profile and bolster its trustworthiness in the eyes of AI.
The interdependence of these AI components for local visibility is profound. No single AI component operates in isolation for generative search; they are deeply interconnected. An LLM’s ability to generate a comprehensive local answer is directly dependent on RAG providing accurate, up-to-date local data. This, in turn, relies on NLP to understand the nuances of a conversational query and to extract relevant information from web content. The Knowledge Graph then validates the entity’s existence and credibility, influencing whether a business is ultimately cited. For local businesses, this means optimizing for just one component (e.g., structured data for the Knowledge Graph) is insufficient. A holistic approach is required where content is not only readable by humans but also semantically rich and structured for machine interpretation across all these AI layers. This implies that traditional SEO elements like structured data and content quality are becoming even more critical, as they serve as the foundational input for these advanced AI systems.
Furthermore, generative AI, particularly for local queries, operates with a strong inherent “trust algorithm.” It is not merely about finding any answer, but rather the most trustworthy answer. This is a direct response to the challenges of misinformation and “hallucinations” that AI models can sometimes produce. RAG systems provide citations, increasing trust and credibility. The Knowledge Graph boosts trust if a brand is consistently described, structured, and cited. Bing Copilot, for instance, grounds its responses in high-ranking web content, heavily weighting features such as relevance, quality, credibility, and freshness. Consequently, local businesses must actively cultivate and signal trustworthiness across all their digital touchpoints. This extends beyond traditional SEO signals to include consistent Name, Address, Phone (NAP) data, positive review sentiment, authoritative citations, and strict adherence to E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) principles. The AI essentially acts as a highly discerning curator, and businesses must unequivocally prove their trustworthiness to be selected as a source.
| AI Technology | Primary Function | Relevance to Local Search |
| LLMs | Text generation, summarization, conversation | Powering AI Overviews and conversational answers for local queries |
| RAG | Real-time data retrieval, context augmentation | Ensuring up-to-date local information and accurate citations |
| NLP | Language understanding, intent analysis, entity recognition | Interpreting local queries, analyzing reviews, extracting details |
| Knowledge Graphs | Entity identification, relationship mapping, fact verification | Verifying local business entities, boosting credibility, powering Knowledge Panels |
III. The Impact of AI-Driven Search on Local Business Visibility
Shifting User Behavior: Conversational Queries and Zero-Click Results
Consumer search behavior is undergoing a rapid transformation. The era of short, mechanical keyword queries is giving way to more fluid, conversational interactions with search tools. Users are now engaging in more natural language, asking longer, more specific questions, and even follow-up questions, much like they would interact with a chatbot. This conversational shift is making search an interactive content experience, where users can convey their needs more naturally than with clunky keyword chains.
A significant consequence of this shift is the rise of “zero-click” results. AI Overviews (AIOs) and generative AI results (GAIRs) provide concise answers and summaries directly on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP), often eliminating the need for users to click through to individual websites. Studies indicate that AIOs now appear in a substantial percentage of Google search results, frequently replacing the traditional click-through behavior. This means that traditional organic listings and local packs may be pushed further down the page, resulting in lower organic Click-Through Rates (CTR) for websites that are not featured prominently in the AI snapshot. The search results page itself is becoming the destination, and the user’s journey often ends there.
Challenges and Opportunities for Local Businesses
The advent of AI-driven search presents both significant challenges and compelling opportunities for local businesses.
Challenges:
- Reduced Web Traffic and Visibility: The most immediate concern is the potential for decreased website traffic. As users obtain direct answers from AI overviews, the necessity to visit a business’s website diminishes. This disruption to traditional traffic metrics can limit opportunities for direct lead capture through a business’s web presence.
- Heightened Competition for AI Visibility: AI-generated results prioritize content that is authoritative, well-structured, and highly credible. This creates an intensified competitive landscape, requiring businesses to invest more heavily in content quality, depth, and strategic presentation to be cited by AI.
- Rapid and Continuous AI Algorithm Changes: The criteria by which AI search engines operate are evolving rapidly and continuously. This dynamic environment necessitates ongoing testing and iteration of optimization strategies, making it challenging for businesses to keep pace.
- Data Insufficiency: AI systems thrive on copious amounts of data for optimal efficiency. Smaller, local businesses often operate with limited data repositories, which can hamper the effectiveness of AI in devising tailored marketing strategies for their specific needs. This data scarcity makes it harder for AI to accurately predict local customer behavior.
- Complexity of AI Algorithms and Limited AI Literacy: Understanding the intricacies of AI and effectively leveraging its capabilities can be a significant hurdle for many local business owners who may lack extensive AI literacy.
- Over-automation Risk: An over-reliance on AI without adequate human oversight can lead to a decline in content quality, diminish customer engagement, and compromise personalized service. AI-generated content, if not properly monitored, may lack the nuance and depth of human-created content.
- Privacy Intrusions: AI systems frequently require access to large datasets to function effectively, which raises significant privacy concerns. This can potentially damage the trust between businesses and their customers if data handling practices are not transparent and secure.
The traditional metric of website traffic (volume) is becoming less indicative of overall business success in the AI era. A lower volume of clicks might actually represent a higher quality of clicks. This implies that local businesses should shift their focus from merely maximizing raw website traffic to maximizing conversion rates from AI-influenced interactions. The emphasis moves towards optimizing for intent and relevance rather than just broad reach. The goal is not simply to be seen, but to be seen by the right people who are already primed with information and ready to take action. This also necessitates the development of new measurement metrics beyond traditional CTR.
Furthermore, the observation that AI flourishes on copious data, which smaller, local businesses often lack, presents a significant hurdle. While larger enterprises benefit from vast data repositories, local businesses frequently operate with limited data, making it more challenging for AI to accurately predict local customer behavior and craft effective, targeted marketing strategies. This requires local businesses to become exceptionally strategic about the data they do collect and how they leverage it. This includes maximizing first-party data (such as customer interactions, reviews, and sales data), diligently maintaining Google Business Profiles, and actively soliciting detailed reviews. It also underscores the importance of human insight to compensate for data gaps, ensuring that AI tools are guided by a deep understanding of local nuances that AI systems may struggle to decipher independently.
Opportunities:
- More Qualified Leads: The conversational nature of AI search allows users to ask more specific and nuanced questions. This means that individuals who discover a business via Search Generative Experience (SGE) are often more highly qualified and thus more likely to convert into customers.
- Room for Niche Players: AI-generated responses tend to prioritize highly relevant and detailed results. This characteristic can be particularly advantageous for small businesses with niche offerings (e.g., a gluten-free bakery or an eco-friendly lawn care service), making it easier for them to stand out in a filtered, intent-driven search environment.
- Reduced Reliance on Ads: As AI-generated answers reduce the number of user clicks on traditional search results, the effectiveness of paid advertisements may diminish. Businesses that successfully optimize their content, reviews, and citations for SGE can benefit from increased organic visibility without incurring the cost of per-click advertising.
- Intent-Rich Discovery: The encouragement of more conversational and specific queries by SGE allows businesses to reach users with higher purchase intent. For example, a query like “late-night pizza places near me with outdoor seating” will prioritize businesses that precisely match this context, leading to more relevant customer connections.
- Enhanced Credibility and Brand Trust: Being cited by an AI overview significantly boosts a business’s credibility and contributes to its overall brand visibility. Knowledge panels, which are powered by Google’s Knowledge Graph, further enhance both visibility and trustworthiness by providing concise, verified information about a business.
- Content as a Visibility Tool: Investing in useful, localized content positions a business as an authoritative source. This increases the likelihood of its content being selected and summarized by AI, making it a preferred source for AI summaries.
- Competitive Advantage: Early adoption of GEO practices can strategically position brands ahead of their competitors in the evolving AI-driven search landscape.
IV. Actionable Strategies for Local Business GEO Success
A. Foundation: Optimizing Your Google Business Profile (GBP) & Local Listings
Optimizing a business’s Google Business Profile (GBP) and other local listings forms the bedrock of a successful GEO strategy. These profiles are fundamental sources of local information that AI models rely on.
- Ensuring Comprehensive and Consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) Data: It is imperative to ensure that every field in a business’s GBP and other online directories is filled out accurately and completely. This includes the business name, address, phone number, website, operating hours, and relevant categories. Google’s AI specifically prioritizes local listings that contain detailed, up-to-date information. Discrepancies in Name, Address, and Phone (NAP) data across different online profiles can confuse AI systems, potentially hindering a business’s visibility in generative search results. Maintaining consistency across all online mentions is therefore crucial for AI interpretation and citation.
- Leveraging High-Quality Visuals and Multimedia: AI models possess the capability to “see” and interpret images. High-quality photographs of a business’s storefront, products, menu items, and services are not only appealing to human users but also build trust and provide essential visual context for AI systems. For achieving multimodal success in AI search, it is vital to support textual content with high-quality images and videos on web pages and within business profiles. These visual elements enhance the richness of information available to AI, making a business more likely to be featured in comprehensive AI-generated responses.
- Proactive Review Management and Sentiment Analysis: Online reviews serve as a rich source of natural language content that AI models can analyze to understand customer sentiment and identify common questions about a business. AI Overviews, in particular, pull heavily from online reviews, especially those that are detailed, positive, and mention key attributes relevant to user queries. Engaging promptly and thoughtfully with customer reviews significantly boosts both a business’s visibility and its trustworthiness in the eyes of AI. Actively managing reviews, encouraging customers to provide feedback, and responding to both positive and negative comments demonstrates engagement and builds credibility. AI-powered tools can greatly assist in this process by scanning hundreds or even thousands of reviews across various platforms, categorizing them by sentiment (positive, mixed, negative), and even drafting response templates to ensure consistency and efficiency in replies.
B. Content is King (and Context is Queen): Crafting AI-Friendly Content
In the generative AI era, content remains paramount, but its context and structure are equally critical for AI interpretation.
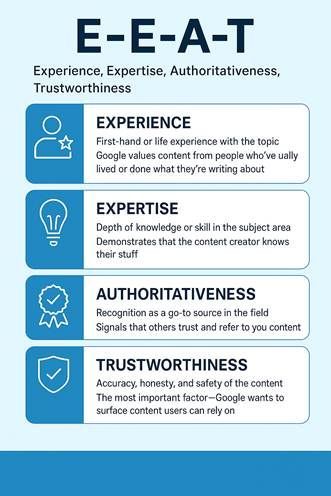
- Prioritizing E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Google explicitly emphasizes content that demonstrates Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). Aligning content with these factors significantly increases its likelihood of appearing in Generative AI Results (GAIRs). AI systems prioritize human-centered, authentic content. This means incorporating personal stories, real-world examples, and case studies to clearly demonstrate hands-on expertise and unique value. The true power of AI for local businesses isn’t in fully automating their marketing, but in acting as an “efficient assistant that never sleeps”. It multiplies human effort by handling repetitive tasks, allowing teams to focus on strategy and creativity. Local businesses should identify specific “headaches” or time-wasters and strategically apply AI tools to those areas (e.g., drafting review responses, generating content outlines, auditing citations). This focused application, combined with human oversight, ensures quality and avoids the pitfalls of generic or unauthentic output. It is about “working smarter, not harder”.
- Optimizing for Conversational Queries and Readability: Content must be crafted to directly answer conversational queries with utmost clarity and readability. Utilizing clear headings, subheadings, and concise paragraphs is essential, as this structure helps AI systems easily parse and present the content within generative results. Writing in a natural, question-and-answer format aligns directly with how users interact with AI tools. The content should focus on problem-solving, positioning the business’s offerings as direct answers to problems potential customers are facing.
- Creating Hyper-Localized and Authentic Content: AI thrives on natural language and content that directly addresses user intent. AI tools can assist in identifying hyperlocal phrases and generating relevant topic clusters, such as “late-night tacos in [local area]” or “authentic French pastries [neighborhood name]”. Businesses should create area-specific landing pages, local blog posts, and dedicated Q&A sections that cater to local needs and interests. Incorporating images or videos of recognizable local landmarks, promoting local events, and targeting local stories and trends are effective ways to make content resonate deeply with the local community. Authenticity is paramount, and leveraging data to drive this authenticity ensures content feels genuinely relevant to the target audience.
- Implementing Structured Data (Schema Markup) for AI Interpretation: Structured data, particularly Schema.org markup, is crucial for conveying information about content in a machine-readable format that AI systems can understand and utilize. It directly helps AI parse and cite content correctly. Businesses should implement relevant schema types, such as LocalBusiness, Restaurant, Product, or Event schema, and apply them to core business information like addresses, hours, and services. It is vital to ensure that structured data accurately matches the visible content on the webpage. Structured data acts as a “universal translator” for AI, allowing it to understand the relationships between entities and the context of information on a webpage, far beyond what plain text can convey. This is how a business can define itself clearly for the Knowledge Graph and for AI Overviews. For local businesses, implementing accurate and relevant structured data is no longer just an SEO best practice; it is a direct communication channel with AI systems. It ensures that critical business information (Name, Address, Phone, services, reviews, events) is explicitly understood by the AI, significantly increasing the likelihood of being featured in direct answers and knowledge panels. This is particularly important for local businesses with unique offerings or specific operating hours, as it provides the AI with precise, unambiguous data.
C. Technical Excellence: Ensuring AI Accessibility
Technical optimization remains a critical component of GEO, ensuring that AI systems can efficiently access and interpret a business’s online content.
- Website Performance and Mobile-First Design: AI systems prioritize well-performing websites. Providing a great page experience is crucial, meaning web pages should be uncluttered, easy to navigate, and display seamlessly across various devices. Fast page load speeds are essential, as both human users and AI systems have limited patience for slow-loading websites. Optimizing images, leveraging caching, and ensuring robust hosting are key steps to achieve rapid load times. Given that a significant portion of searches occur on mobile devices, a mobile-first design approach is not merely good practice but a strong signal of a well-maintained and user-centric online presence.
- Crawlability and Indexability for AI Systems: Businesses must ensure their web pages meet the technical requirements for Google Search, enabling search engines to find, crawl, and index their content effectively. This includes verifying that Googlebot is not blocked, that pages return a successful HTTP 200 status code, and that the content is indexable. Content that adheres to fundamental SEO principles, such as clear metadata and semantic search optimization, is significantly more likely to be retrieved and utilized by Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)-powered AI systems. Meeting these technical requirements provides a foundational layer for general search visibility, including for AI formats.
D. Building Authority & Trust Signals for AI Citation
Establishing authority and trust is paramount for encouraging AI systems to cite a business’s content.
- Strategic Citation Building and Directory Management: Consistent Name, Address, Phone (NAP) data across the entire web, particularly on authoritative third-party directories like Yelp, TripAdvisor, and the Better Business Bureau (BBB), is critical for AI visibility. AI-powered crawlers can perform bulk citation audits, scan the web for references to business information, and identify and resolve duplicate listings, which can confuse AI systems. These tools can also assist with automated submission to geo-targeted directories, ensuring broad and consistent local presence.
- Effective Link Building and Brand Mentions: Inbound links from credible and relevant sources continue to reinforce a business’s authority in the eyes of search engines and AI. Strong brand mentions through various forms of content, media coverage, and strategic partnerships are also vital signals of trustworthiness and relevance. AI tools can help identify potential link targets and even draft personalized pitches for outreach. Cultivating a strong reputation by being reliable, useful, and having a pervasive online presence helps AI systems trust and prioritize a brand’s information. Ultimately, being cited by AI directly boosts a business’s credibility, making these authority-building efforts directly contribute to GEO success.
V. Leveraging AI Tools for Local GEO
AI tools are becoming indispensable for local businesses seeking to optimize for generative search. They act as efficiency multipliers, automating tedious tasks and providing data-driven insights.
AI-Powered Tools for Content Creation and Optimization
Generative AI tools can automate content creation, streamline campaign optimization, and enhance customer engagement through personalized messaging. Tools such as Jasper AI, ContentShake AI, and Notion AI can significantly assist with copywriting, blog post generation, and overall productivity. These tools can quickly draft content for area-specific landing pages, localized blog posts, and comprehensive Q&A sections, accelerating the content production pipeline. Furthermore, AI can suggest improvements for metadata, including headlines, title tags, and meta descriptions, enhancing readability, keyword placement, and click-through appeal. For visual content, platforms like Invoke and Stable Diffusion WebUI offer capabilities for local image generation, allowing businesses to create high-quality, relevant visuals efficiently.
AI for Keyword Research and Topic Clustering
AI can dramatically expedite keyword research by analyzing vast volumes of data and suggesting relevant ideas that might be missed through manual efforts. Specialized tools can scrape search patterns and autocomplete suggestions across multiple ZIP codes or neighborhoods, identifying hyperlocal phrases like “late-night tacos in [local area]”. AI can also analyze historical Google Trends data to forecast seasonal fluctuations in search demand and generate logical topic clusters (e.g., grouping “best hiking trails near Denver,” “family-friendly hiking spots near Denver,” and “gear rental for Denver hikes”) to make content planning more systematic. Additionally, AI can perform competitor analysis, extracting top keywords and content themes from competing local websites to identify content gaps or opportunities to outrank others. Examples of tools that offer such capabilities include BrightEdge’s Instant and Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool.
AI for Reputation and Review Management
AI tools are transforming how local businesses manage their online reputation. They can efficiently scan hundreds or even thousands of customer reviews across various platforms, automatically categorizing them and analyzing sentiment (positive, mixed, or negative). This capability allows businesses to quickly understand customer perceptions at scale. AI can also draft response templates for reviews, ensuring a consistent brand tone and integrating relevant keywords into replies. Platforms like Center AI and Reputation.com consolidate reviews from multiple sources into a single dashboard, automate responses, and provide actionable insights to optimize reputation management strategies. These tools are designed to help businesses increase the volume of positive reviews, improve the overall quality of feedback, and curtail negative reviews by offering private channels for customers to share concerns before they become public.
AI for Local Listing and Citation Management
Maintaining accurate and consistent local listings is paramount for GEO, and AI tools can significantly streamline this process. AI-powered crawlers can perform bulk citation audits, systematically scanning the web for references to a business’s information and identifying any inconsistencies or duplicate listings. They can also assist with automated submission to geo-targeted directories, ensuring a business’s presence across relevant local platforms. Tools like Localo and Search Atlas offer comprehensive features for managing and optimizing Google Business Profiles, including generating Q&As for GBP listings and monitoring local rankings with precision. This automation saves considerable time and effort, ensuring that foundational local data is always accurate and consistent, which is crucial for AI systems.
Considerations for Local LLM Deployment (Privacy, Cost, Hardware)
Running Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on a business’s own infrastructure, rather than relying solely on cloud-based services, offers distinct advantages, particularly for local businesses.
- Privacy: Local LLM deployment ensures that sensitive data remains entirely under the user’s control, which can be a prerequisite for compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. This is crucial for businesses handling confidential customer information (e.g., healthcare, legal, financial services) or proprietary internal data, as it prevents external exposure that can occur with cloud-based LLMs.
- Reduced Latency: Since data processing occurs locally and is not dependent on network calls to cloud servers, response times are generally faster, assuming adequate hardware. This low latency can enhance real-time applications and user experiences.
- Lower Operating Costs: While there is an initial investment in hardware, running LLMs locally can lead to lower operating costs over time compared to the pay-as-you-go models of cloud-hosted APIs, which can increase significantly with usage. Local deployment also eliminates vendor lock-in.
- Customization and Offline Availability: Local LLMs offer full control over model fine-tuning and domain-specific optimizations, allowing businesses to tailor models precisely to their unique needs. They also function without an internet connection, providing offline availability for critical tasks.
However, local deployment comes with significant hardware requirements . Running LLMs locally demands substantial computing resources, specifically GPUs with high VRAM capacity and a considerable amount of RAM. For instance, a 7B model may require at least 8 GB of RAM, while larger models might need 32 GB or even 64 GB of DDR4/DDR5 RAM. This initial hardware setup represents a notable upfront cost. Despite these requirements, user-friendly tools like Ollama, Jan.ai, and LM Studio simplify the process of downloading and running open-source LLMs directly on personal computers.
The strategic advantage of local LLMs for sensitive local data is clear. For local businesses dealing with sensitive customer data or proprietary internal information, using cloud-based LLMs for certain tasks presents significant privacy and security risks. Local LLMs provide a secure environment for processing such data without external exposure. This implies that while cloud LLMs are convenient for general tasks, local businesses should consider investing in local LLM setups for tasks involving confidential customer interactions (e.g., personalized service suggestions based on private data) or internal knowledge base queries (e.g., indexing internal documentation for staff training). This allows them to leverage AI’s power while maintaining strict data sovereignty and compliance, ultimately building greater trust with their local customer base.
| Category | Tool Examples | Primary Function for Local GEO | Key Benefit for Local Business |
| Content Creation & Optimization | Jasper AI, ContentShake AI, Invoke, Notion AI | Generate localized content drafts, suggest metadata improvements | Time savings, improved content relevance, consistent branding |
| Keyword Research & Topic Clustering | BrightEdge Instant, Semrush, Localo, Search Atlas | Identify hyperlocal keywords, analyze competitors, generate topic clusters | Enhanced targeting, discovery of niche opportunities |
| Reputation & Review Management | Center AI, Reputation.com, Localo | Analyze review sentiment, draft responses, increase review volume | Enhanced customer trust, improved online image, efficient feedback management |
| Local Listing & Citation Management | Localo, Search Atlas | Manage GBP listings, audit citations, generate Q&As | Increased local visibility, accurate information across platforms |
| General AI Assistants/Productivity | Ollama, LM Studio, Jan.ai, Notion AI | Automate tasks, assist with research, provide local LLM deployment | Efficiency gains, cost reduction, data privacy |
VI. Ethical Considerations in Local GEO
The integration of generative AI into local business marketing brings forth several critical ethical considerations that must be proactively addressed to maintain trust and authenticity.
Addressing Bias and Fairness in AI-Generated Content
AI algorithms are trained on vast historical datasets, which may inadvertently contain or reflect existing societal biases and inequalities. This inherent bias can manifest in AI-generated content, leading to discriminatory outcomes, perpetuating stereotypes, or misrepresenting certain demographics. To mitigate these risks, businesses must conduct regular bias assessments of their AI outputs, ensuring that the generated content is fair and equitable. Implementing diverse review teams to scrutinize AI-generated material is crucial, as is documenting all bias mitigation efforts. Establishing clear guidelines for content moderation and maintaining transparency about the limitations of AI are also vital steps to ensure ethical content creation.
Protecting Data Privacy and User Information
The operational efficiency of AI systems often relies on access to large volumes of data, which raises significant privacy concerns. Key privacy risks include unauthorized data access, exposure of personal information, vulnerabilities to data breaches, cross-contamination of information, and unintended data memorization by AI models. Local businesses must ensure strict compliance with all relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, as well as industry-specific privacy standards and local privacy laws. Implementing robust security measures and adopting transparent practices for data collection and usage are essential to safeguard user information and build customer trust.
Ensuring Authenticity and Combating Misinformation
The rapid advancement and increasing sophistication of generative AI make it increasingly challenging for users to discern what is real from what is fabricated online. AI has the capacity to generate deepfake content, fabricate narratives, manipulate statistics, and create false attributions. For local businesses, maintaining authenticity and credibility is paramount, as their success often hinges on community trust and personal relationships. It is crucial to prioritize authentic, user-generated content and proactively manage online reviews to establish and reinforce trust. Implementing rigorous content verification protocols, including fact-checking procedures and source validation, is vital. Utilizing authentication systems like digital watermarking and provenance tracking can help verify the origin and integrity of content. Furthermore, disclosing AI usage when appropriate and maintaining detailed content creation logs contribute to transparency and accountability.
Ethical AI practices are not merely about compliance; they are becoming a significant competitive differentiator, especially for local businesses that rely heavily on community trust and personal relationships. A local business that transparently uses AI, rigorously protects customer data, and consistently ensures content authenticity will likely build stronger trust and loyalty compared to one that does not. Therefore, local businesses should actively communicate their ethical AI practices to their customers. This could involve clear privacy policies, disclaimers on AI-assisted content, and a public commitment to human oversight in content creation and decision-making processes. By demonstrating a strong ethical stance, businesses can enhance their brand reputation, attract privacy-conscious customers, and gain a unique advantage in a market where trust is an increasingly valuable commodity.
VII. Measuring Success & Adapting to the Future
New Metrics for AI-Influenced Search
The shift to generative AI search necessitates a re-evaluation of how success is measured. Traditional SEO metrics such as organic Click-Through Rates (CTR) may experience a decline due to the prevalence of “zero-click” results, where users find answers directly within AI overviews. Consequently, new metrics are emerging as crucial indicators of performance in the AI-driven landscape:
- AI Overview Citations: This metric tracks how often a business’s content is cited or summarized within AI Overviews. Being cited significantly boosts a business’s credibility and overall visibility, even if it doesn’t immediately lead to a click-through to the website.
- Brand Mentions in AI Responses: Monitoring how frequently a brand is mentioned by various AI platforms, including generative AI tools like ChatGPT or Google’s AI-powered results, provides valuable insight into brand recognition and AI visibility.
- Sentiment of AI Mentions: Beyond mere mentions, it is crucial to analyze the sentiment with which a brand is described by these AI platforms. This ensures that the AI’s portrayal aligns with the desired brand perception and helps identify any potential reputational issues.
- Engagement with AI-Generated Content: While direct clicks may decrease, tracking user interaction with AI summaries that feature a business’s information can still provide valuable data on how effectively the AI is conveying the brand’s message.
- Conversion Rates from AI-Influenced Traffic: Given that AI-influenced leads are often more qualified due to conversational and precise queries, focusing on the conversion rates of these leads becomes more important than raw traffic volume.
- Domain Authority (DA) and Credibility: AI tools tend to prioritize businesses with a reasonable or high Domain Authority and strong overall credibility, reinforcing the importance of foundational SEO and trust-building efforts.
The traditional metric of “website traffic” (volume) is becoming a less accurate measure of success. The true return on investment (ROI) of GEO might be “hidden” in the quality of interactions and conversions, even if direct website visits decrease. This requires a fundamental shift in how businesses measure success. Local businesses need to develop sophisticated tracking mechanisms that go beyond simple website analytics. This includes meticulously monitoring AI citations, analyzing brand sentiment in AI responses, and, most importantly, correlating AI visibility with tangible business outcomes such as actual sales, direct inquiries, or increased foot traffic. This redefines what “visibility” truly means in the AI era, moving the focus from mere impressions to impactful engagements.
Continuous Testing and Iteration in a Rapidly Evolving Landscape
The AI search landscape is inherently dynamic, with search criteria and algorithms evolving at a rapid pace. This necessitates a commitment to continuous testing and iteration of GEO strategies. Businesses must actively monitor their AI mentions and adjust their strategies accordingly. Analyzing AI-generated search traffic, such as identifying AI-related referrals in Google Analytics, allows businesses to adapt their approach based on what AI systems prioritize and how users interact with AI results. Google’s AI, for instance, continually learns from user interactions, constantly adjusting how it ranks and generates responses. Therefore, businesses must evolve alongside their users and the AI systems that serve them.
The observation that AI search criteria evolve rapidly and that a brand can become “suddenly invisible” if not surfaced by AI highlights a critical business mandate. The dynamic nature of AI algorithms means that a “set it and forget it” SEO strategy is no longer viable. Continuous monitoring, testing, and adaptation are not just best practices but a fundamental requirement for maintaining online visibility. Local businesses must foster a culture of continuous learning and agility in their marketing efforts. This includes regularly auditing their online presence, staying informed about the latest AI search updates, and being prepared to pivot strategies quickly in response to algorithmic shifts. Those who fail to adapt risk being completely bypassed by AI systems, effectively disappearing from the new search landscape.
Real-World Success Stories and Case Studies of Local Businesses Thriving with GEO
While specific, large-scale “local business GEO” case studies are still emerging as the field matures, numerous examples demonstrate how local businesses are successfully adopting AI for efficiency and improved customer experience, which directly contributes to their overall digital presence and readiness for GEO.
- A print shop owner, facing challenges with endless customer quotes and design revisions, implemented a basic AI tool integrated with Google Docs to automate the first draft of customer quotes. This simple solution, costing around $50 a month, saved the business 15 hours of work in the first month and doubled its conversion rate within three months by enabling faster responses to customers.
- A bakery successfully used AI to predict daily sales, resulting in a 30% reduction in waste by optimizing inventory and production.
- A freelance designer significantly improved efficiency by automating client email responses using AI, freeing up time for more creative tasks.
- A local gym leveraged AI to personalize workout plans for its members, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement.
- A small e-commerce brand saw remarkable improvements in its email marketing, with open rates increasing by 35% and revenue from email campaigns jumping by 50% after integrating AI-powered predictive analytics and personalization.
- Some brands have reported cutting their Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) by nearly half through AI-driven ad optimization tools like Meta Advantage+ and Google’s Performance Max, which efficiently test different creatives and audience segments.
These examples, while not exclusively categorized as “GEO” in the traditional sense, powerfully illustrate how AI can solve specific, tangible business problems, leading to measurable improvements in efficiency, customer experience, and ultimately, overall growth. The underlying principle for local businesses is to identify a specific “headache” or time-consuming task and then seek out simple, cost-effective AI solutions to address that particular problem. This pragmatic approach allows businesses to gradually integrate AI, measure tangible improvements, and build confidence in leveraging these technologies for broader digital optimization.
VIII. Conclusion: Embracing the AI Search Era for Local Growth
The digital landscape is undeniably transforming, with generative AI reshaping how users search for information and discover businesses. For local businesses, understanding and adapting to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is not merely an option but an essential strategic imperative for sustained visibility and growth.
Key Takeaways for Local Businesses:
- GEO is an Evolution, Not a Replacement: Generative Engine Optimization represents the essential evolution of search marketing. It complements and enhances traditional SEO by focusing on how AI-driven search engines interpret and present information, rather than replacing foundational SEO practices.
- Prioritize Trust and Authenticity: AI systems prioritize authoritative, credible, and human-centered content. To be cited by AI, businesses must build strong trust signals through consistent Name, Address, Phone (NAP) data across all platforms, adherence to E-E-A-T principles, comprehensive structured data implementation, and proactive, authentic review management.
- Optimize for Conversational Intent: The shift in user behavior towards conversational queries means content strategy must adapt to directly and comprehensively answer natural language questions. This involves creating content that is readable, contextually rich, and anticipates user follow-up questions.
- Leverage AI Tools Strategically: AI tools serve as powerful efficiency multipliers for various marketing tasks, including content drafting, keyword research, and reputation management. However, their deployment should always be accompanied by human oversight to ensure quality, authenticity, and alignment with brand values.
- Embrace New Measurement Paradigms: Traditional metrics like click-through rates may become less relevant. Businesses should shift their focus to tracking AI citations, brand mentions within AI responses, and, most importantly, the quality and conversion rates of leads generated through AI-influenced search.
- Cultivate Continuous Adaptation: The AI landscape is dynamic and rapidly evolving. Regular monitoring of AI search trends, continuous testing of GEO strategies, and iteration based on performance data are crucial for maintaining sustained visibility and competitive advantage.
Actionable GEO Checklist for Local Businesses:
To thrive amidst generative AI search shifts, local businesses must be proactive in adopting GEO principles. The journey begins with a strategic approach to their digital presence:
Google Business Profile & Local Listings:
- Complete all Google Business Profile fields with accurate and comprehensive information (NAP, hours, categories).
- Upload high-quality photos and videos of the business, products, and services.
- Actively manage and respond to all customer reviews, encouraging detailed and positive feedback.
- Ensure NAP consistency across all online directories and citation sources.
Content Strategy:
- Develop content that demonstrates Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
- Craft content in a natural, conversational tone, directly answering common customer questions.
- Create hyper-localized content that incorporates local landmarks, events, and community-specific nuances.
- Implement relevant structured data (Schema.org) for all key business information and content types.
Technical SEO:
- Ensure the business website is mobile-first and fully responsive across all devices.
- Optimize for fast page load speeds to provide a superior user experience.
- Verify that the website is fully crawlable and indexable by search engine bots.
Authority & Trust:
- Strategically build citations on authoritative third-party directories.
- Actively seek and secure brand mentions through local media, partnerships, and community engagement.
- Cultivate a strong online reputation by consistently providing value and reliability.
AI Tool Integration:
- Identify specific “pain points” or time-consuming tasks within marketing operations.
- Explore and pilot simple, cost-effective AI tools to automate or assist with these tasks (e.g., AI for drafting review responses, generating content ideas, or auditing citations).
- Consider local LLM deployment for tasks involving sensitive customer data or proprietary internal information, prioritizing data privacy.
By systematically addressing these areas, local businesses can effectively navigate the complexities of generative AI search, enhance their digital presence, and secure a prominent position in the evolving answer-driven search landscape. The future of local business growth is intrinsically linked to embracing and mastering Generative Engine Optimization.
Works cited
1. Generative Engine Optimization: The Future of SEO – Mailchimp, https://mailchimp.com/resources/generative-engine-optimization/
2. What Is Generative Engine Optimization? Meaning & Origin – Ramp, https://ramp.com/blog/what-is-generative-engine-optimization
3. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): Mastering AI-Driven Search in 2025 – SOCi, https://www.soci.ai/blog/generative-engine-optimization/
4. How Search Generative Experience Will Affect Local SEO – Writesonic Blog, https://writesonic.com/blog/search-generative-experience
5. How AI Overview Affects Local Search and Your SEO Strategy – M&R Marketing, https://www.mandr-group.com/how-ai-overview-affects-local-search-and-your-seo-strategy/
6. How AI is Reshaping Search Behaviour (and What Marketers Should Do to Adapt), https://www.accuracast.com/articles/search-articles/ai-changing-search-behaviour/
7. A Deep Dive Into GEO: How It Differs From Traditional SEO | Brandignity, https://www.brandignity.com/2025/04/a-deep-dive-into-geo-how-it-differs-from-traditional-seo/
8. AI Search Evolution: GEO vs Traditional SEO – TheeDigital, https://www.theedigital.com/blog/generative-engine-optimization-geo-vs-seo
9. Copilot in Bing: Our approach to Responsible AI – Microsoft Support, https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/copilot-in-bing-our-approach-to-responsible-ai-45b5eae8-7466-43e1-ae98-b48f8ff8fd44
10. How is Google Gemini Enhancing Search Capabilities? – Thunder::Tech, https://www.thundertech.com/blog-news/how-is-google-gemini-enhancing-search-capabilities
11. Any reliable ways to track generative engine optimization? : r/SEO – Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/SEO/comments/1ll0ucs/any_reliable_ways_to_track_generative_engine/
12. The Future of Search: How LLMs Are Changing Google | SiteGuru, https://www.siteguru.co/seo-academy/ai-seo-strategy-shift
13. Understanding RAG and SEO: The Future of Generative AI – Trust Signals, https://www.trustsignals.com/blog/understanding-rag-and-seo-the-future-of-generative-ai
14. Understanding RAG: Retrieval Augmented Generation Essentials for AI Projects – Apideck, https://www.apideck.com/blog/understanding-rag-retrieval-augmented-generation-essentials-for-ai-projects
15. What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation aka RAG – NVIDIA Blog, https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/what-is-retrieval-augmented-generation/
16. Natural Language Processing Examples That Affect SEO, https://www.hikeseo.co/learn/technical/natural-language-processing-examples
17. NLP in SEO: What It Is & How to Use It to Optimize Your Content – Semrush, https://www.semrush.com/blog/nlp-seo/
18. Understanding Google Knowledge Graphs – Global Lingo, https://global-lingo.com/understanding-google-knowledge-graphs/
19. The Impact of Knowledge Panels on Local SEO and How to Improve Your Visibility – Indexsy, https://indexsy.com/knowledge-panel/
20. Ethical Considerations When Using Generative AI – Magai, https://magai.co/ethical-considerations-when-using-generative-ai/
21. Boosting your small business visibility in the AI search era – PayPal, https://www.paypal.com/us/brc/article/boosting-your-small-business-visibility-in-the-ai-search-era
22. How AI Is Changing Local Search – Advice Local, https://www.advicelocal.com/blog/how-ai-changing-local-search/
23. Top ways to ensure your content performs well in Google’s AI experiences on Search, https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2025/05/succeeding-in-ai-search
24. Challenges of AI in Marketing to Local Businesses – BuzzBoard, https://www.buzzboard.ai/challenges-of-ai-in-marketing-to-local-businesses/
26. Generative Search Best Practices for Small Businesses – Marketing …, https://blog.marketing360.com/general-marketing-tips/generative-search-best-practices-for-small-businesses/
27. Unique Strategies To Use Generative AI To Get Better Local SEO Results – Emulent, https://emulent.com/blog/unique-strategies-to-use-generative-ai-to-get-better-local-seo-results/
28. Reputation Management Software – Center AI, https://center.ai/solutions/reputation-management-software/
29. How to rank in AI search – a guide for small business – Happy Pedals, https://happypedals.ca/blog/how-to-rank-in-ai-search-a-guide-for-small-business/
30. Small Business AI Success Stories You Need to Know In 2025, https://ldms-intl.com/small-business-ai-success-stories/
31. Generative AI for Marketing: Tools, Examples, and Case Studies | M1-Project, https://www.m1-project.com/blog/generative-ai-for-marketing-tools-examples-and-case-studies
32. What are some success stories of using AI in digital marketing? : r/DigitalMarketing – Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/DigitalMarketing/comments/1joskam/what_are_some_success_stories_of_using_ai_in/
33. Localo | Best Local SEO Tool & Software – [Choose free plan], https://localo.com/
34. Hyperlocal Social Media Marketing: What You Need to Know – Solutions | Rent., https://solutions.rent.com/blog/hyperlocal-social-media-marketing
35. How to Create Hyperlocal Marketing Content | Built In, https://builtin.com/articles/create-hyperlocal-marketing-content
36. Cutting through the noise: AI’s real impact on local search | DAC, https://www.dacgroup.com/insights/blog/local-optimization/cutting-through-the-noise-ais-real-impact-on-local-search/
37. 26 best AI marketing tools I’m using to get ahead in 2025, https://www.marketermilk.com/blog/ai-marketing-tools
38. Invoke | Generative AI Platform for Creative Production, https://www.invoke.com/
39. Setting Up Local Generative AI Tools – Machines and Society, https://guides.nyu.edu/data/ai-local
40. Top 10 SEO AI Use Cases with Case Studies in 2025 – Research AIMultiple, https://research.aimultiple.com/seo-ai/
41. Reputation | Online Reputation Management for Business, https://reputation.com/
42. Search Atlas: The #1 AI SEO Automation Platform for Agencies and Brands, https://searchatlas.com/
43. How to run Large Language Models (LLMs) locally. – DEV Community, https://dev.to/theelitegentleman/how-to-run-large-language-models-llms-locally-1ngc
44. Local large language models (LLMs) and their growing traction – Pieces for Developers, https://pieces.app/blog/local-large-language-models-lllms-and-copilot-integrations
45. Mastering AI Ethics: Small Business Operation Strategies, https://www.movingforwardsmallbusiness.com/mastering-ai-ethics-small-business-operation-strategies/
46. How Local Businesses Are Winning AI Search (And Why You’re Invisible) – Medium, https://medium.com/@thomas_berkley/how-local-businesses-are-winning-ai-search-and-why-youre-invisible-abfe7469d9a0








